COMPUTER-ASSISTED STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF REGULAR GLYCOPOLYMERS
ON THE BASIS OF 13C NMR DATA
N. D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
KEYWORDS: glycosylation effect, database, chemical shift, polysaccharide, structure, NMR, computer
Carbohydrate Research, 2001, v. 335 (2), pp.101-114
DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6215(01)00214-2
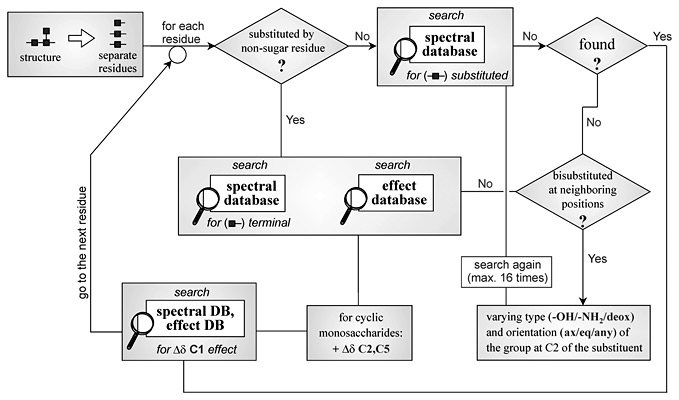
The computer-assisted approach to the prediction of the primary structures of regular biopolymers is described. The analysis is based on comparing the semitheoretical 13C NMR spectra of all the possible structures of the repeating unit (for the given monomeric composition) to the experimental 13C NMR spectrum. The spectra generation is based on the spectral database containing information on the 13C chemical shifts of monomers, di- and trimeric fragments. If the required data are missing from this database, the special database for average glycosylation effects is used. The analysis reveals the structures with generated 13C NMR spectrum most close to observed. The structures of repeating units of any topology containing up to 6 residues linked by glycosidic, amidic or phospho-diester bridges can be predicted. Testing the created program and databases on bacterial polysaccherides and their derivatives containing up to three non-sugar residues (alditols, aminoacids, phosphate groups etc.) per repeating unit revealed the good convergence of predictions with independently obtained structural data.